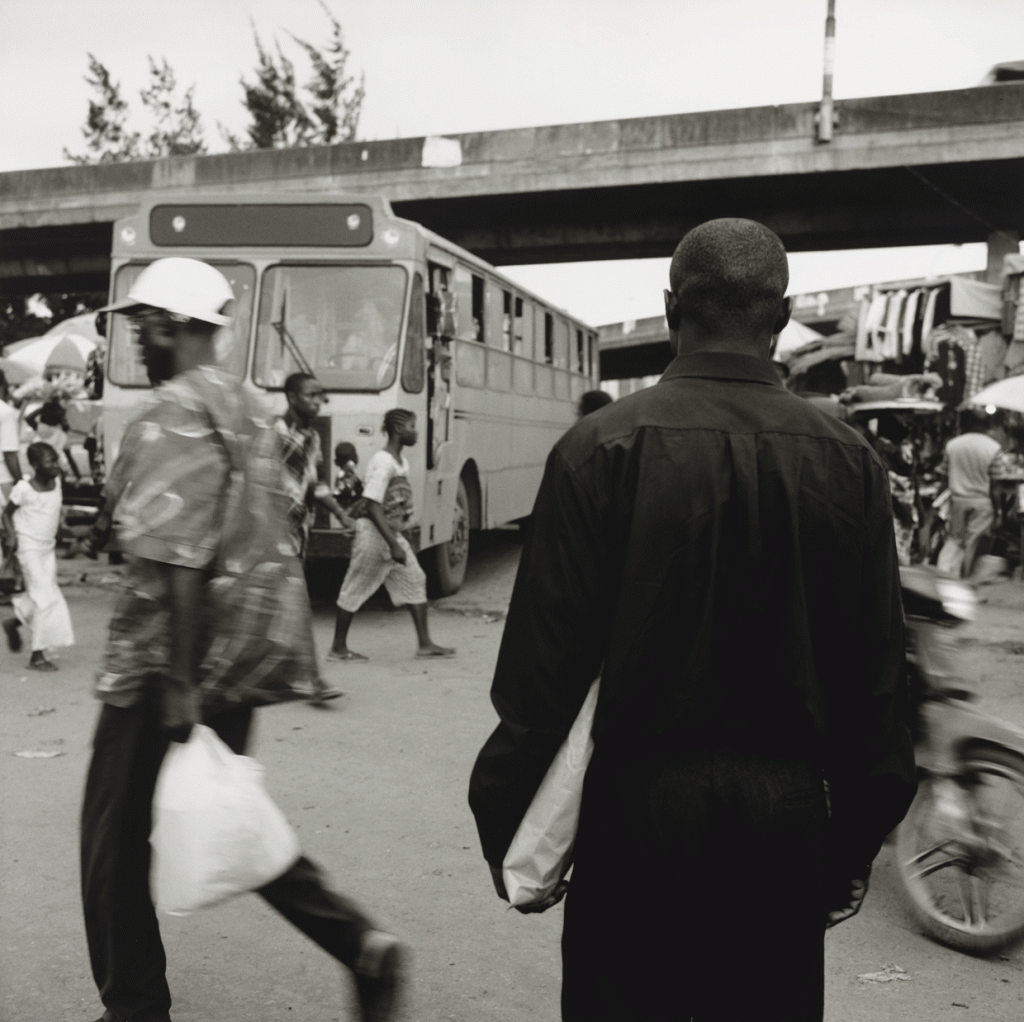 Laongo CSPS Clinic, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture, Philadelphia Museum of Art
Laongo CSPS Clinic, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture, Philadelphia Museum of Art
The Architecture of Francis Kéré, Building for Community, Philadelphia Museum of Art
May 14 – September 25, 2016, Collab Gallery, Philadelphia Museum of Art
Francis Kéré is an internationally renowned, Berlin based architect who integrates traditional knowledge and craft skills into innovative and sustainable buildings worldwide. As the first son of the head of Gando, his home village in Burkina Faso, he was the only child allowed to attend school in a large city; he later studied architecture in Europe. While still a student, he began to reinvest his knowledge back into his community, building schools that would change its future trajectory.
In Gando, Kéré combined traditional Burkinabé building techniques with modern engineering methods, maximizing local materials and community participation to reduce costs and ecological impact—a practice common to many of the projects highlighted in this exhibition. His work in Gando has become a catalyst for further development: the men and women he trained in construction techniques can now use their skills to earn incomes for their families. Students in his schools have gone on to pursue higher education and aspire to circumstances that were considered impossible before.  Primary school in Gando, Burkina Faso, completed 2001, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph by Erik-Jan Ouwerkerk
Primary school in Gando, Burkina Faso, completed 2001, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph by Erik-Jan Ouwerkerk
Harnessing the success of the Gando initiative, Kéré founded his Berlin office in 2005 and has since garnered acclaim for his work elsewhere in Western Africa and, more recently, in Europe and North America. He is the recipient of the 2014 Schelling Architecture Foundation Award, the Global Award for Sustainable Architecture, and the BSI Swiss Architectural Award, among others.
 Gando School Library, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture
Gando School Library, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture
This school consists of nine modules that house a series of classrooms and administrative offices. The laterite stone walls, undulating off-white ceiling, and unique wind-towers exponentially reduce the interior temperature.
Secondary School, 2007 / Dano
Consisting of three classrooms, a computer room, and office space, this school is built mostly of widely available laterite stone and features a permeable ceiling, a corrugated sheet roof, and shaded windows that ensure natural ventilation. The laterite refining process and the ventilation system illustrate Kéré’s innovative techniques utilizing local handicraft.
 Gando School Extension, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph by Erik-Jan Ouwerkerk
Gando School Extension, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph by Erik-Jan Ouwerkerk
Primary School , 2001 / Gando
To ensure a natural and sustainable cooling system in an extremely hot region, the roof over the classrooms is elevated from the interior construction; underneath, a perforated clay ceiling allows for maximum ventilation.
Canopy Shelter and Shade
The tree is a primal form of shelter. Four fundamental elements of architecture can be extracted from the various parts of the tree: canopy, structure, gathering place, and shadow. The canopy, as a general concept of various roof and ceiling enclosures, is an architectural cornerstone in Kéré’s work. Constructions in hot, arid places like Burkina Faso depend on innovative shade-making devices that allow ventilation and cooling without the need for electricity, as well as overhangs that provide protection from torrential rains. This video’s skyward perspective presents the importance of canopies in Burkina Faso, from village trees to traditional ceilings made of clay and thatch, to Kéré’s roof constructions at different stages of completion.
 Gando School Library, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture
Gando School Library, Designed by Francis Kéré, Burkinabe, active Berlin, Photograph © Kéré Architecture
Building with Community
Reflecting the accessibility of Kéré’s building process, this video shows one of his most recent projects: the Lycée Schorge school in Koudougou, Burkina Faso. Unlike most modern construction sites in the West, which are strictly off-limits to the public, the Schorge site is left open for the surrounding villagers to observe. This process demystifies the act of building, allowing the public to slowly accept and sometimes even contribute to the new construction. Every stage of the project, including mounting the ceiling trusses and facade elements, fabricating the classroom furniture, and painting the interiors and window shutters, is performed without the use of heavy machinery.
The chairs in this space were made by a local fabricator in Philadelphia using the same design that Kéré created for schools in Burkina Faso. The Francis Kéré Foundation and the Philadelphia Museum of Art are pleased to offer these fifteen chairs for sale at the close of the exhibition to support Kéré’s further work in Gando. If you would like to reserve one or more chairs, please visit the Museum Store in this building for further details.
Diébédo Francis Kéré: How to build with clay… and community
Sharing Knowledge
Whether in a classroom with chalkboards and desks, or under a great baobab tree with logs and stones, the survival and prosperity of each new generation relies heavily on the transmission of knowledge. Gathering is not only a function of social occasions, it is also how ideas are discussed and spread. Shadow symbolizes this place of coming together. Visitors are invited to sit within this gathering space.
Wood
While natural hardwood forests are rare in Burkina Faso, the fast-growing eucalyptus tree provides a useful source of timber. This species is considered a nuisance in the region because it provides little shade and leaches moisture from the soil, exacerbating the problems of desertification. Despite its limited structural strength, it can still be made into screens, interior finishes, furniture, and even secondary facade systems that shade and protect buildings from wind and rain. Through the process of testing and prototyping, Kéré’s firm is also exploring new solutions for reinforcing the material for structural applications.
Clay
Burkinabés have long built with clay, extracting it from the earth, processing it by hand, and using it in a variety of architectural and craft elements, from walls to hand-built pottery. For the Gando School Library, Kéré pioneered a new use for local clay, casting sections of large pots into the ceiling to provide natural ventilation and lighting. Made by local women, the pots were transported to the building site on foot, involving the community’s expertise and participation. More recently, Kéré engineered an innovative way to cast the clay into reusable molds, creating wall systems that can be replicated for use in modular buildings.
Bricks
Bricks play a crucial role in Kéré’s architectural practice. Whether cast from clay or cut from locally extracted laterite stone, the simple form of the brick can be used to create sophisticated architectural forms and building systems. With or without mortar, bricks can be used in walls, ceilings, and floors. Different systems of stacking and bonding can produce a permeable boundary, allowing air and light to pass through. Thick brick walls also create a thermal mass, which, together with adequate ventilation and shading, helps to maintain a comfortably cool interior space.
School Furniture
To offset the costs of transporting building materials to remote sites with extremely limited means, Kéré and his team came up with ingenious ways to use every scrap of material left over from construction. Using steel rebar and plywood, the team built customized chairs and desks for school students and staff. Every bend and weld was carefully calculated to streamline production time and costs. The furniture was produced on-site with simple hand tools and jigs. A particularly striking detail is the rubber “shoe” made by hand from recycled automobile tires.
Architecture of Community
Despite the many differences between the city of Philadelphia and the village of Gando in Burkina Faso, where Francis Kéré was born, the installation in this atrium emphasizes the human-scale domestic architecture of both places and the sense of community such a design produces. In the plan of this space, Kéré overlaid the geometric grid of William Penn’s Philadelphia — represented by the regular placement of the frames that support the hanging parachute cord enclosures — with the irregular disposition of the enclosures themselves, mimicking the organic development of a Burkinabé village. The installation also features sounds collected from both Burkina Faso and Philadelphia, reinforcing the concept of community and shared space. The hanging parachute cord material may appear first as an obstacle, but on entering and interacting with the installation, the visitor will perceive that the material is a unifying, enclosing element that creates common spaces that must be negotiated and shared.
It Takes a Village
Conceived by Kéré Architecture and designed in collaboration with the Philadelphia Museum of Art’s Curatorial, Exhibition Design, and Editorial and Graphic Design teams, this exhibition has fostered an exchange of ideas, traditions, and experiences between Africa, Europe, and the United States. Thanks to the eager participation of many members of the Museum staff and volunteers, the Young Friends Executive Board and event committee, students from the University of Pennsylvania Undergraduate Program in Architecture, and the general public to help fabricate components, this installation truly represents the coming together of a community. In addition, the Philadelphia Museum of Art would like to acknowledge Richard Wesley, for facilitating the UPenn collaboration; Larry Spitz, Carol Klein, and Sasha Barrett, who generously offered their services in creating the red clay pots to suggest the Gando Library ceiling; and David Cann and James Bassett-Cann, for their help in the realization of the atrium installation.
Photography is OK, but please no flash.
Social Media: #CreativeAfrica
Follow us and join the conversation: Twitter/Facebook/Instagram/Tumblr/YouTube@philamuseum
The Philadelphia Museum of Art is Philadelphia’s art museum. We are a landmark building. A world-renowned collection. A place that welcomes everyone. We bring the arts to life, inspiring visitors—through scholarly study and creative play—to discover the spirit of imagination that lies in everyone. We connect people with the arts in rich and varied ways, making the experience of the Museum surprising, lively, and always memorable. We are committed to inviting visitors to see the world—and themselves—anew through the beauty and expressive power of the arts.
Thank you to The Philadelphia Museum of Art for the content of this post.
SEO and Photoshop by DoN.
Like DoNArTNeWs Philadelphia Art News Blog on facebook
Follow the new DoNArTNeWs.com
Follow DoN on Twitter @DoNNieBeat58
DoNArTNeWs on Tumblr
@donniebeat on Instagram
Affiliate Marketing [disclosure page] Shop on-line and help support DoNArTNeWs
Donate via safe and secure PayPal in the sidebar.