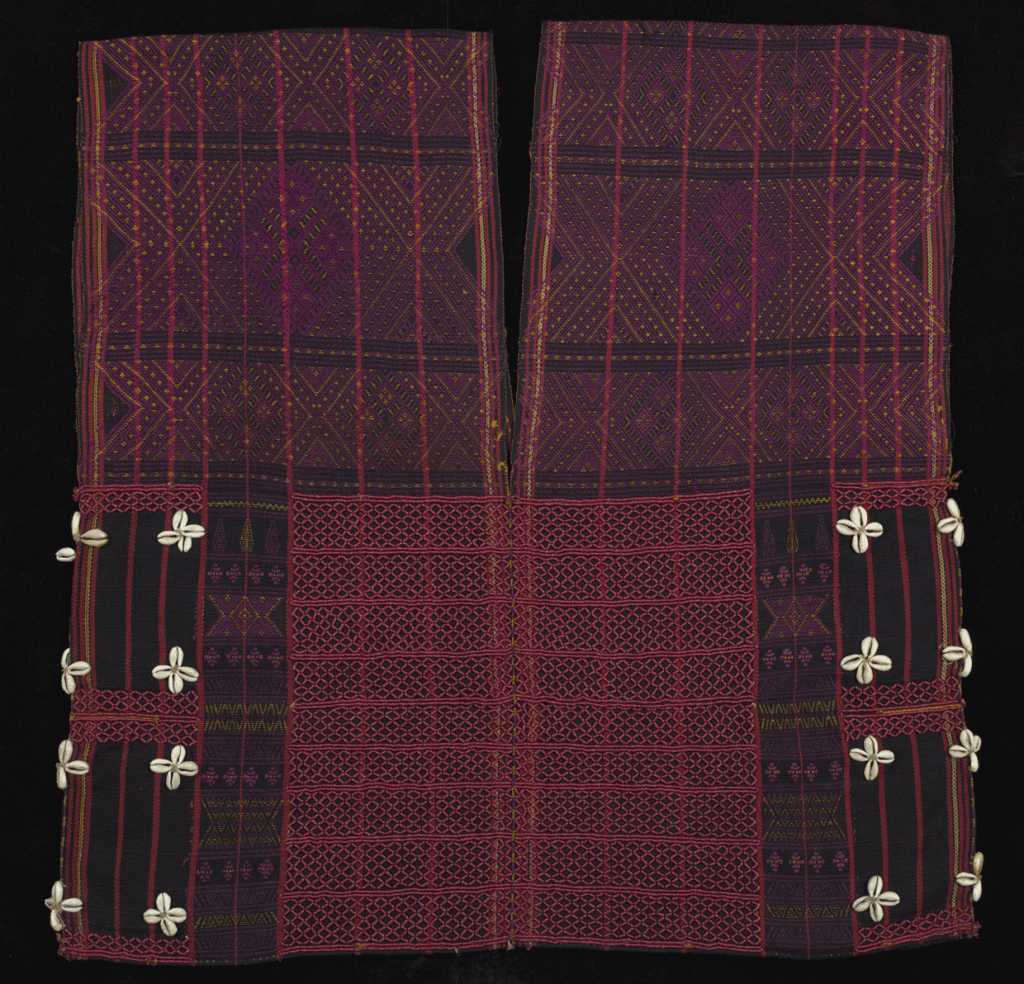
Tota Bagh Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, buttonhole, and chain stitches, 7 feet 8 3/4 inches × 56 inches (235.6 × 142.2 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
Tota Bagh Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, buttonhole, and chain stitches, 7 feet 8 3/4 inches × 56 inches (235.6 × 142.2 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
Phulkari: The Embroidered Textiles of Punjab
from the Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Collection, Joan Spain Gallery, Perelman Building, Philadelphia Museum of Art
Phulkari: The Embroidered Textiles of Punjab from the Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Collection
Through July 9, 2017
Phulkari, meaning “flower work” (phul = flower, kari = work), is an embroidery originally made throughout Punjab, a region now straddling Pakistan and India. Traditionally, the base cloth was locally handspun and handwoven cotton called khaddar. The thread, called pat, was unplied silk usually imported from China. The dominant embroidery stitch is the darning stitch (a straight stitch in parallel rows), although artists interspersed it with other stitches. Perhaps because of thread’s high cost, most pieces show embroidery only on one side of the cloth.
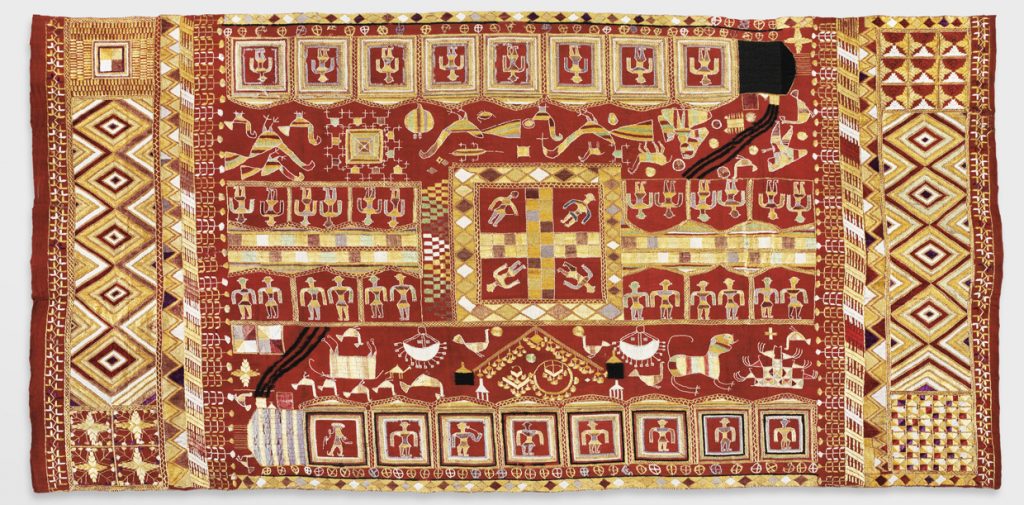
 Sainchi Phulkari/Nilak Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, running, chain, and buttonhole stitches, glass mirrors, 7 feet 5 inches × 53 inches (226.1 × 134.6 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Sainchi Phulkari/Nilak Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, running, chain, and buttonhole stitches, glass mirrors, 7 feet 5 inches × 53 inches (226.1 × 134.6 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Phulkaris were a crucial part of a Punjabi woman’s material wealth. Young girls learned needlework from their older female relatives and friends. Often they made phulkaris for their own dowries, which they brought with them to their husbands’ home when they married. Primarily intended as large shawls worn draped over the head, phulkaris could also function as bedding or wall hangings for special functions. While each phulkari is unique, they may be grouped into types by designs and background colors with names such as thirma (white), sainchi (figurative), or bagh (garden).
 Darshan Dwar Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, pattern darning, buttonhole, herringbone, running and Cretan stitches, 7 feet 5 inches × 50 inches (226.1 × 127 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Darshan Dwar Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, pattern darning, buttonhole, herringbone, running and Cretan stitches, 7 feet 5 inches × 50 inches (226.1 × 127 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Highlighted here are nineteen superb phulkaris from the Bonovitz Collection, promised gifts to the Philadelphia Museum of Art. All were probably created before the Partition of Pakistan and India in 1947. Also included is a small selection of traditional phulkaris from the Museum’s permanent collection. The exhibition concludes with a creative twenty-first century reinvention of phulkari in the high fashion garments of Manish Malhotra, one of India’s leading designers.
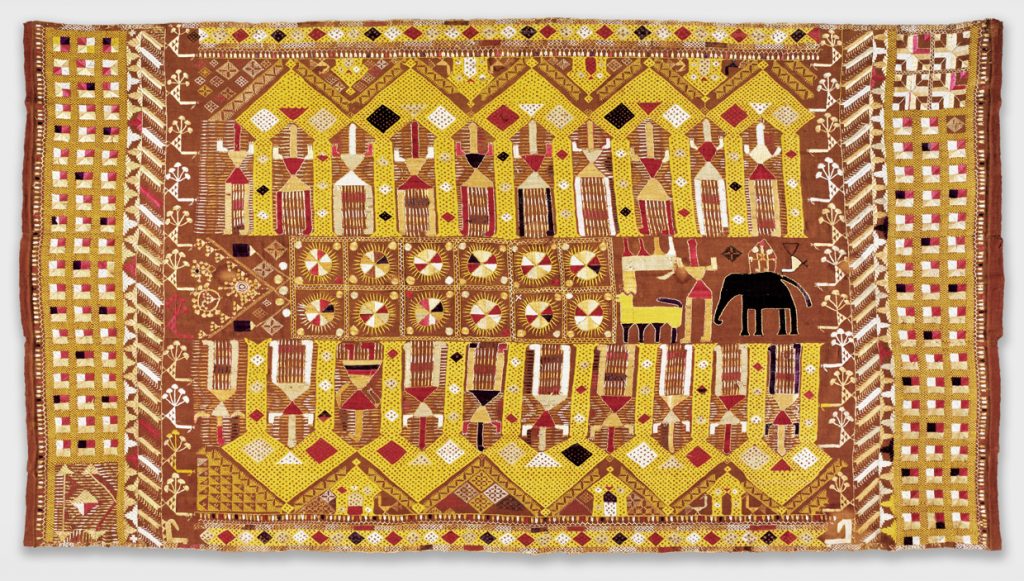
 Sainchi Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk, cotton, and wool embroidery in darning, pattern darning, buttonhole, herringbone, running, chain and Cretan stitches, 7 feet 5 1/2 inches × 48 1/2 inches (227.3 × 123.2 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Sainchi Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk, cotton, and wool embroidery in darning, pattern darning, buttonhole, herringbone, running, chain and Cretan stitches, 7 feet 5 1/2 inches × 48 1/2 inches (227.3 × 123.2 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
This exhibition is made possible by Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz, The Coby Foundation, Ltd., and The Stella Kramrisch Indian and Himalayan Art Fund.
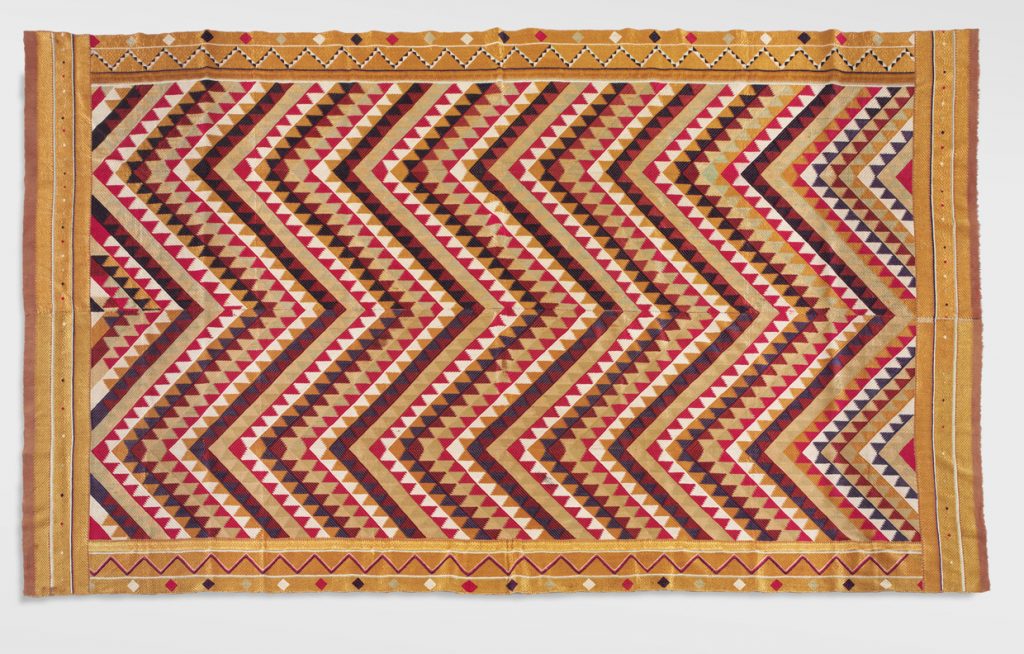 Bagh Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in darning, pattern darning, running, chain and cross stitches, 8 feet 3 3/4 inches × 59 1/2 inches (253.4 × 151.1 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
Bagh Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in darning, pattern darning, running, chain and cross stitches, 8 feet 3 3/4 inches × 59 1/2 inches (253.4 × 151.1 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
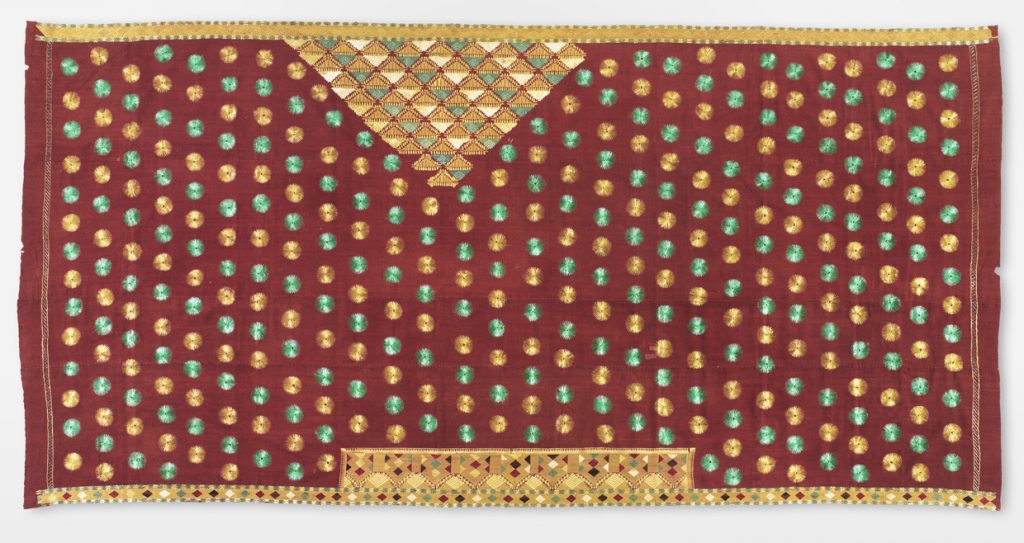 Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in running, darning, pattern darning, herringbone, split, stem and cross stitches, 9 feet 5 inches × 58 inches (287 × 147.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in running, darning, pattern darning, herringbone, split, stem and cross stitches, 9 feet 5 inches × 58 inches (287 × 147.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
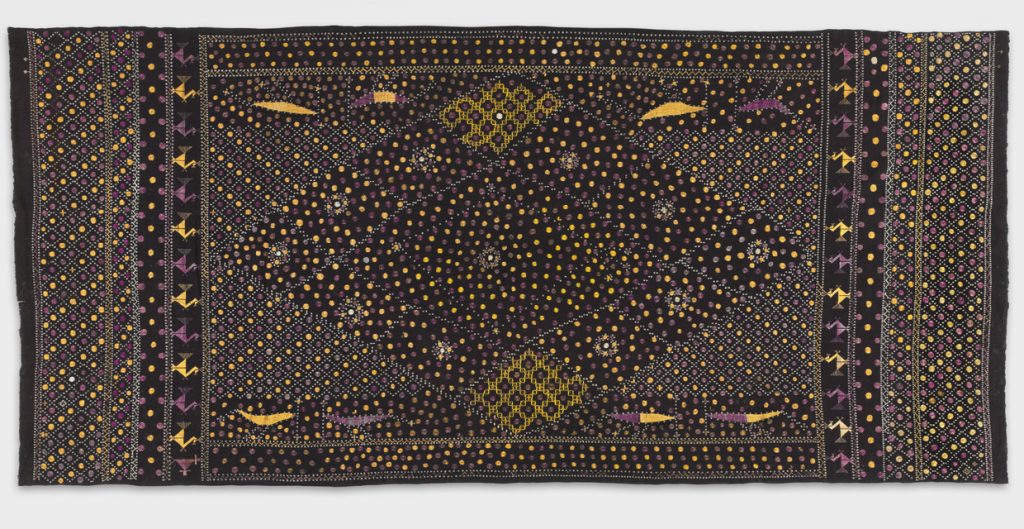 Phulkari, Early 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, running, herringbone, and double running stitches, 8 feet 6 1/2 inches × 47 1/2 inches (260.4 × 120.7 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Phulkari, Early 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning, running, herringbone, and double running stitches, 8 feet 6 1/2 inches × 47 1/2 inches (260.4 × 120.7 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
 Thirma Phulkari, 19th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in darning, whip, and running stitches, 8 feet 5 inches × 58 inches (256.5 × 147.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
Thirma Phulkari, 19th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in darning, whip, and running stitches, 8 feet 5 inches × 58 inches (256.5 × 147.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection.
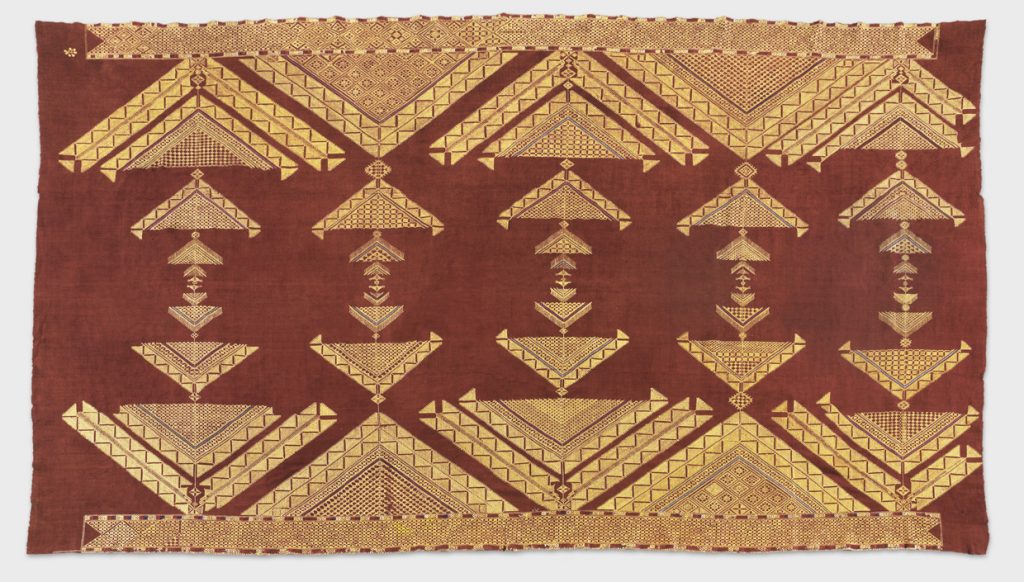 Chope Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in double running stitch, 9 feet 8 inches × 69 inches (294.6 × 175.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Chope Phulkari, 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun cotton plain weave (khaddar) with silk embroidery in double running stitch, 9 feet 8 inches × 69 inches (294.6 × 175.3 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
 Sainchi Phulkari, Early 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning and chain stitches, 8 feet 3 inches × 52 inches (251.5 × 132.1 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
Sainchi Phulkari, Early 20th century. Artist/maker unknown, Punjabi. Handspun, handwoven plain weave (khaddar) with silk and cotton embroidery in darning and chain stitches, 8 feet 3 inches × 52 inches (251.5 × 132.1 cm). The Jill and Sheldon Bonovitz Phulkari Collection. (click for large image)
——————–
1947 to Today
When India gained independence from Great Britain in 1947, Punjab was divided—its western part in Pakistan and its eastern in India. The devastating results of Partition left many millions dead, injured, and displaced. Most families lost their heirloom phulkaris and few women had the time or facilities to embroider, apart from occasional commercial work. Over the past sixty years, Punjabis of all religions—Muslims, Hindus, Christians, and Sikhs (a faith whose holy sites are located in Punjab)—have emigrated throughout South Asia and around the world. Today they are the largest South Asian diaspora. Phulkari embroidery has retained enormous emotional and symbolic significance for all Punjabis and it has been reenvisioned in many ways.
Thank you to The Philadelphia Museum of Art for the content of this post.
Like The Philadelphia Museum of Art on facebook
SEO and Photoshop by DoN.
Like DoNArTNeWs Philadelphia Art News Blog on facebook
Follow the new DoNArTNeWs.com
Follow DoN on Twitter @DoNNieBeat58
@donniebeat on Instagram
Affiliate Marketing [disclosure page] Shop on-line and help support DoNArTNeWs